The Importance of Air Quality in Food Production
With the arrival of spring, pollen and airborne particles increase, making air quality a critical factor for food safety. An efficient ventilation and filtration system reduces contamination from microorganisms, dust, and allergens, ensuring a safe environment for food production.
Main Risks of Poor Air Quality
- Contamination by pollen, mold spores, and bacteria in the production process.
- Risk of pathogen spread through the air, such as Salmonella and Listeria.
- Presence of fine particles (PM2.5 and PM10) that can compromise food safety.
- Cross-contamination between different production areas.
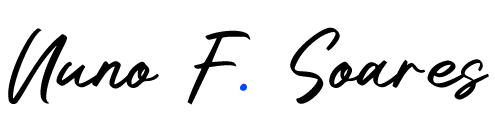
Air Quality Standards and Requirements
Air quality in food factories must comply with international standards such as ISO 16890-1:2016 and Eurovent 4/23-2022, which define supply air (SUP) categories and filtration levels based on outdoor air quality (ODA).
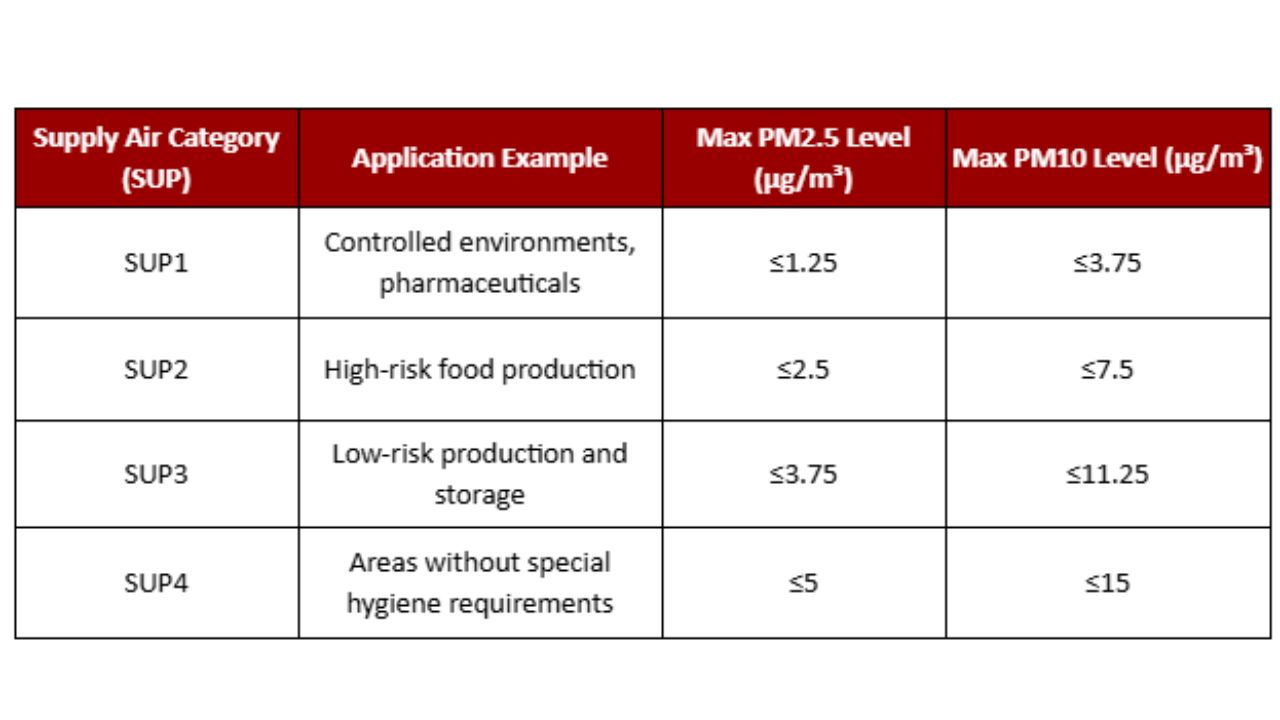 Air Filtration in the Food Industry
Air Filtration in the Food Industry
The level of air filtration should match the type of production. The Eurovent 4/23-2022 recommends the following minimum filters:
Best Practices for Ensuring Air Quality
- Perform regular maintenance and replacement of air filters
- Monitor PM2.5 and PM10 levels with appropriate sensors.
- Implement separate zones for different risk levels
- Assess outdoor air quality before it enters the ventilation system.
- Consider HEPA filters for sensitive areas.
Air Quality Monitoring Recommendations
To better understand seasonal variations, it is advisable to conduct at least two air quality analyses per year—one in the spring, when pollen and airborne particles are at their peak, and another in a different season for comparison. This helps identify trends and necessary adjustments in filtration and ventilation systems.
Conclusion
Air quality is an invisible but essential ingredient in food production. With a proper ventilation system and effective filters, we can reduce contamination risks and ensure a safe environment for both workers and consumers.